According to a Microsoft Report, 90% of consumers expect brands to offer an online self-service support portal.
That’s because web self-service puts the power in the customer’s hands.
Instead of waiting on hold or writing long emails, people can turn to website self-service options to instantly get the necessary answers.
From intelligent chatbots to detailed help centers, these tools are changing how support is done.
In this article, we’ll break down how web self-service works and review the best self-service portal for your business. Let’s begin.
What is Web Self-Service?
Web self-service is a digital customer support system that allows users to solve problems on their own, without talking to a live agent. It lives on your website and empowers customers to get answers instantly.
It includes tools like knowledge bases, chatbots, and self-service portals built into your site. These modern solutions cater to users who expect quick, 24/7 help.
By offering fast, independent support, businesses not only reduce ticket volume but also increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Web Self-Service Statistics
Here are some statistics related to web self-service that will give you an idea on why it’s so important for your business:
1. In fact, a study by the Harvard Business Review found that 81% of customers try to resolve issues themselves before ever reaching out to support.
2. Gartner Survey Reveals Just 14% of Customer Service Issues Get Fully Resolved via Self-Service.
3. Customers were unable to find relevant content in 43% of failed self-service attempts, making it the most frequent reason for failure.
4. Clients using ServiceTarget, a customer support platform, report a 45% average boost in customer satisfaction after implementing its self-service tools.
5. Chatbots could reduce customer support costs by as much as 30%, potentially saving $23 billion in the U.S. by automating a larger share of contact center tasks.
6. The TDWI Best Practices Report: Self-Service BI surveyed 587 professionals, mainly IT staff, consultants, and business users.
When asked which features were most important in a self-service BI environment, respondents ranked the following:
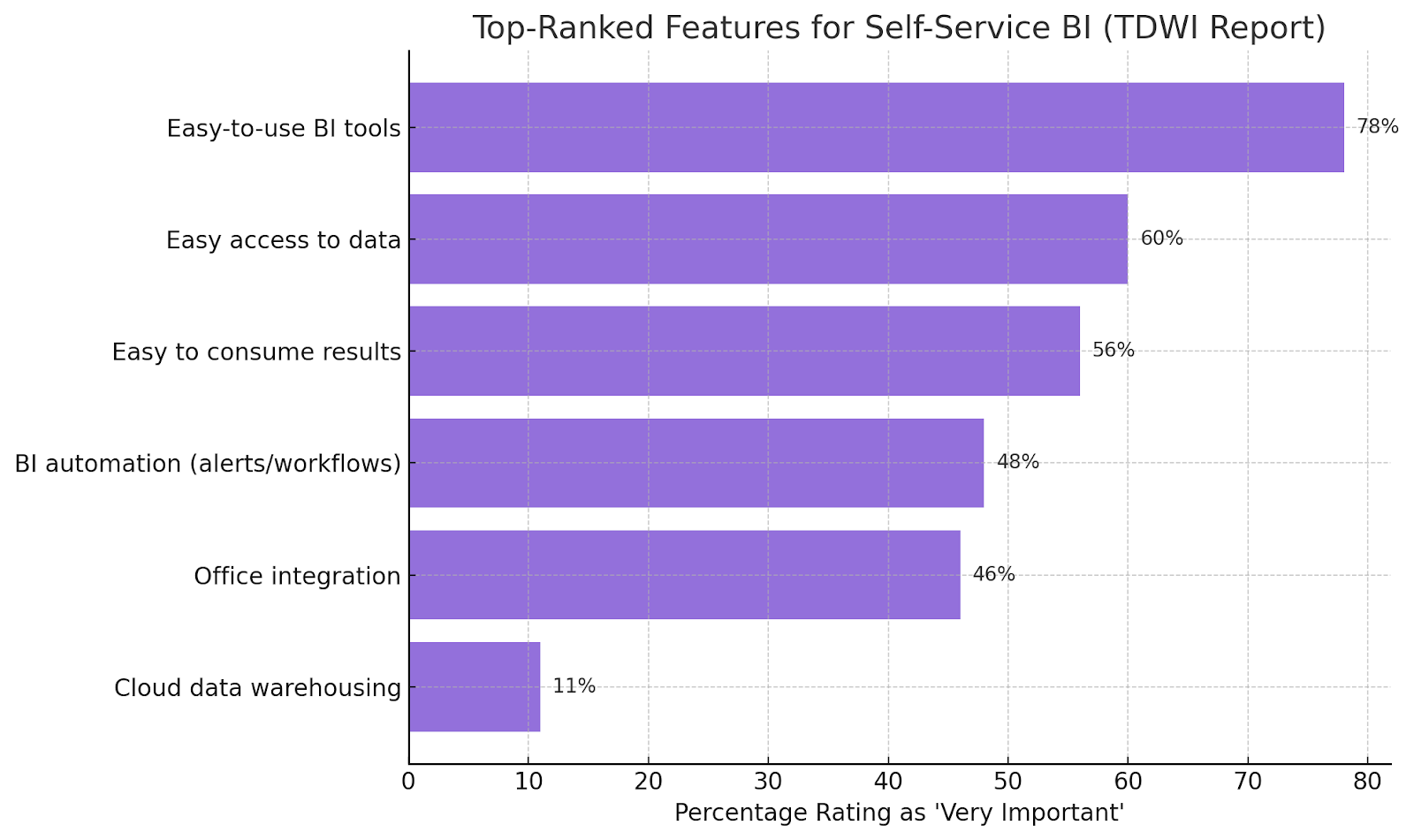
The respondents also identified the following as the biggest barriers to implementing self-service tools:
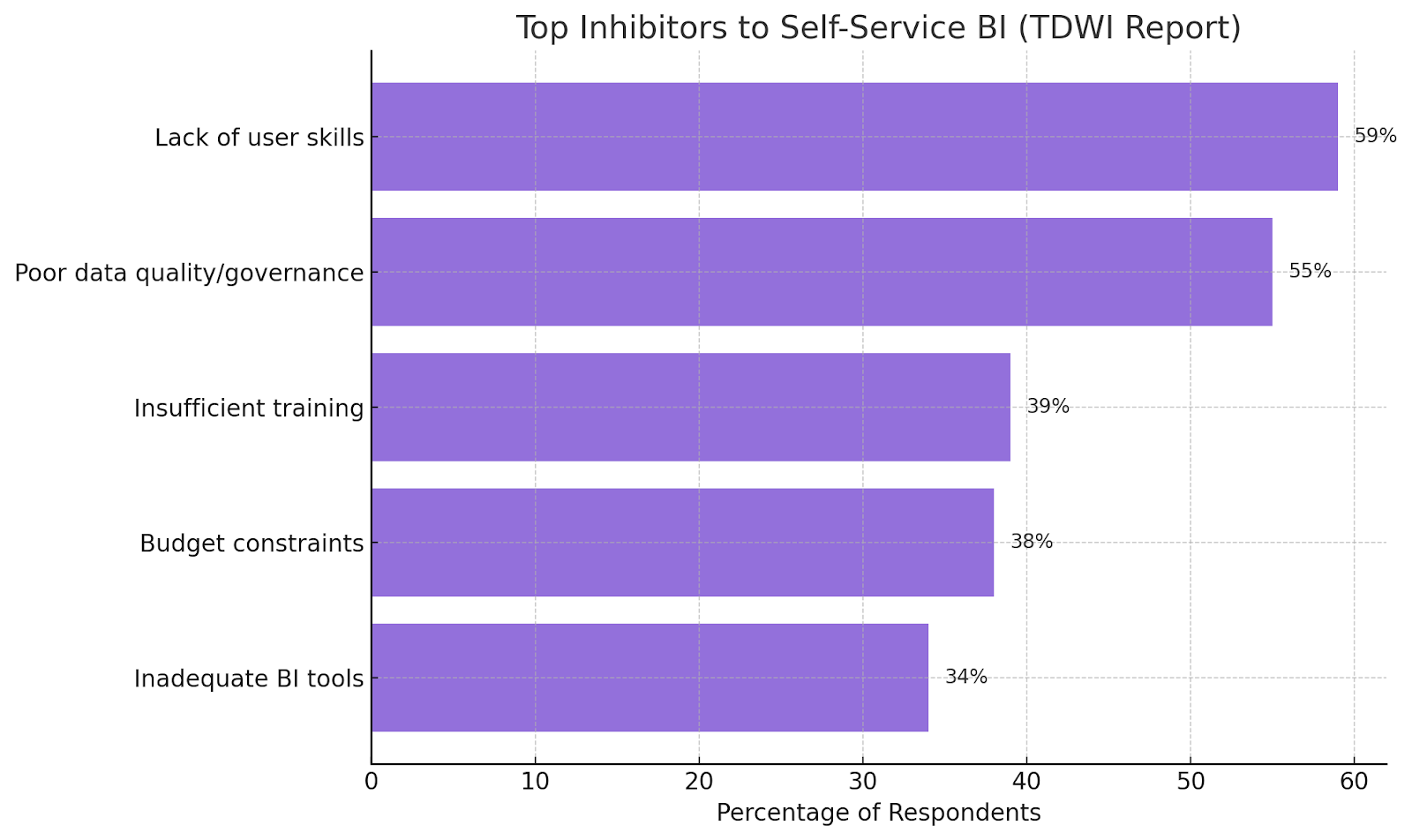
How Does Self-Service Work?
Web self-service lets customers solve issues on their own, or it fails. Here’s how the process typically works from the user’s perspective:
1. Customer encounters a problem or question: They might need help with billing, a product feature, resetting a password, or tracking an order.
2. They go to the company’s website or app: Instead of calling or emailing support, they open the business’s support portal, help center, or homepage.
3. They look for the self-service section: This is usually labeled something like “Help Center,” “Support,” or appears as a chatbot icon or search bar.
4. They describe the issue: The customer might type a question (e.g., “how do I update my payment method?”) or click on categories that match their issue.
5. The system responds with relevant resources: The system displays step-by-step articles, videos, or answers from a knowledge base. The chatbot replies directly.
6. Customer follows the guidance: They use the instructions provided to complete the task. Such as changing a setting, downloading a form, or updating their profile.
7. Issue resolved—no agent involved: If the content or guidance was accurate and easy to follow, the customer fixes the issue on their own and leaves satisfied.
Or,
(If unresolved) They escalate to live support: If the answer isn’t helpful, the system may offer a quick way to contact an agent. This can be through chat, email, or a callback.
Web Self-Service vs Traditional Support: What’s the Difference?
Investing in self-service tools reduces costs in the long term, but there’s an initial cost. Understanding the key differences helps teams decide when and where each method works best to make it cost-efficient.
| Aspect | Web Self-Service | Traditional Support |
| Availability | 24/7 access, allowing customers to resolve issues at any time. | Limited to business hours, restricting customer support to specific times. |
| Cost per Interaction | Approximately $0.40 per self-service interaction. | Around $8 per interaction with a human agent. |
| Customer Preference | 73% of customers prefer to solve issues independently. | 27% prefer interacting with a human representative. |
| Speed | Immediate responses, enabling quick issue resolution. | Potential wait times due to queues and agent availability. |
| Personalization | Moderate; relies on algorithms and predefined responses. | High; agents can provide tailored solutions based on customer interaction. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to handle increasing customer queries without proportional cost increases. | Limited by the number of available support staff, leading to higher costs with scale. |
| Customer Satisfaction | 77% of customers have a more positive view of organizations offering self-service options. | Satisfaction depends on agent efficiency and availability. |
| Resolution Rate | 14% of issues are fully resolved through self-service. | Higher resolution rates due to direct human intervention. |
Types of Web Self-Service
Web self-service comes in different variations. And it’s better to have multiple self-service options, but before that, you should know which one does what.
Naturally, there are four major types of self-service:
1. Knowledge Base

A knowledge base is a structured collection of self-serve support content that answers customer questions and explains how to use a product or service.
Think of it as your business’s digital reference library. It’s organized, searchable, and always available.
This content usually includes FAQs, step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting articles, glossary terms, how-to guides, and sometimes videos or diagrams.
For many companies, the knowledge base is the primary point of contact for support. It’s often accessed via the help center or embedded in product UIs through tooltips, widgets, or search bars.
Use Cases
A knowledge base has these three potential use cases:
- Customers use it to find answers on their own, from basic questions to advanced how-tos. It helps them get things done quickly without opening a ticket or waiting in a queue.
- Prospects browse it to understand your product before making a purchase. A well-maintained knowledge base builds trust by showing that your platform is transparent, documented, and easy to navigate.
- Support agents rely on it to speed up responses and ensure consistency. Instead of drafting replies from scratch, they can share articles that walk users through the solution.
How to Build Your Knowledge Base
Building an effective knowledge base isn’t just about writing articles. Here’s a practical approach to your own:
1. Start with Your Support Data
Pull reports on your most frequently asked questions. Use ticket tags, chat transcripts, or call logs to identify topics that repeat. This ensures you’re writing articles your customers need.
2. Structure It Around Tasks, Not Departments
Group your content by customer goals, not internal processes. For example, use categories like “Getting Started,” “Account Management,” or “Troubleshooting” instead of “Sales” or “Engineering.”
3. Write for Clarity, Not Brilliance
Each article should focus on solving one problem. Use headings, numbered steps, screenshots, and plain language.
4. Choose the Right Platform
You can build a knowledge base using:
- Help desk tools like Zendesk, Freshdesk, or Help Scout
- CMS plugins for WordPress or HubSpot
- Standalone tools like Document360, GitBook, or Notion
These platforms allow for search, tagging, analytics, and access control, key for scaling your content.
5. Keep It Alive
Set up a process to review and update articles regularly. Support reps should be encouraged to flag outdated content. Analytics (like article views or drop-offs) help spot what’s not working.
2. Customer Portal

A customer portal is a secure, personalized dashboard where customers can log in to manage their relationship with your business.
Unlike a public knowledge base, customer portals are private and account-specific, designed to give users control over their data, requests, and interactions.
Think of it as the customer’s command center. From tracking orders and managing subscriptions to downloading invoices or submitting tickets, a portal informs customers of everything post-purchase.
What Customers Can Do in a Portal
Customer portals offer varying levels of functionality depending on the business type, but most include:
- Track order or service status
- Access billing history, invoices, and payment options
- Submit and monitor support tickets
- Download purchased resources or completed deliverables
- Manage subscriptions or service plans
How to Build a Customer Portal
Creating a portal that’s helpful, secure, and easy to use requires thoughtful planning and the right tools. Here’s a framework to start:
1. Choose a Platform That Matches Your Needs
You can download a plugin and set up a client portal on your WordPress website or choose a 3rd party solution like Agency Handy. A dedicated software is faster to set up and has more features. Plus, it looks more polished.
Agency Handy gives you:
- Branded client login
- Project tracking dashboard
- File sharing and deliverable access
- File Feedback and revision workflow
- Invoice viewing and payment
- Support ticket submission
- CRM and billing integration
- Role-based access control
2. Customize Based on Your Needs
Add your business details and customize your client portal. Set up the sign up page, log-in page, canned emails, invoice template, service catalog, etc. Add the embeddings or integrations needed to personalize individual client portals.
3. Use Role-Based Access Control
Not all customers need to see the same information. Define user roles so that admins, team members, or billing contacts each access what’s relevant to them.
4. Invite Clients
Start inviting your clients through email and help them with onboarding.
3. Community Forum

A community forum is an interactive space where your customers can connect, ask questions, exchange tips, and share experiences. It’s usually placed in a publicly accessible part of business websites.
It acts as a peer-to-peer support channel and knowledge-sharing hub. These forums also become powerful feedback loops.
You get real-time insights into what matters to your users, what’s confusing, what they love, and how they use your product.
How to Build Your Community Forum
Setting up a community forum requires more than opening a discussion board. You need structure, consistency, and a community mindset. Here’s how to do it:
1. Start with Clear Discussion Categories
Define 4–6 broad topics your users care about (e.g., “Getting Started,” “Advanced Tips,” “Integrations,” “Feedback & Ideas”). This gives conversations a home and prevents chaos.
2. Seed the Forum with Helpful Threads
Have your team start initial conversations, such as FAQs, “Show us your setup,” or “What’s your biggest challenge?” These spark engagement and show users what kinds of posts are welcome.
3. Write Clear Guidelines
Set expectations on tone, relevance, and behavior. Keep it simple, focus on respect, clarity, and staying on topic. Pin these rules to every category or in a dedicated Welcome section.
4. Moderate Consistently
Assign team members to monitor the forum. They don’t need to reply to everything, but should enforce rules and remove spam. Positive, visible moderation sets the tone for respectful discourse.
4. Chatbots and AI Assistants

Chatbots and AI-powered assistants are real-time conversational tools that help customers get answers, complete actions, or navigate services.
Unlike static help articles or portals, chatbots simulate a live conversation, guiding users step by step, 24/7.
Depending on how advanced they are, they do the following:
- Answer FAQs
- Route requests
- Collect information
- Escalate to human agents
- Generate personalized recommendations
Benefits of Adding Chatbots to Your Website
Here’s why you most businesses in 2025 should include chatbots as part of their customer support strategy:
- 24/7 Availability: Chatbots offer round-the-clock assistance, answering questions and resolving issues anytime, day or night.
- Cost Savings: By automating routine tasks, chatbots can save businesses up to 2.5 billion working hours.
- Improved Customer Experience: Approximately 60% of business owners believe that AI chatbots can help to improve their customers’ experience.
- High Adoption Rates: As of 2024, approximately 60% of B2B companies and 42% of B2C companies currently use chatbot software.
- Market Growth: The global AI chatbot market is expected to reach $46.64 billion by 2029, growing at a 24.53% CAGR. Stationia
Here’s a table to select web self-service for your business:
| Type | Description | Best For | Key Benefit |
| Knowledge Base | A collection of helpful articles, FAQs, and how-to guides | SaaSTecheCommerceStartups | Reduces ticket volume and educates users |
| Customer Portal | Where users manage their accounts and info | B2BFinanceHealthcareSubscription services | Secure login and quick access |
| Community Forum | Peer-to-peer discussion and support platform | GamingTechLifestyle brandsWeb hosting | Builds loyalty and scales community support |
| Chatbots & AI Assistants | Instant answers from automated chat or voice assistants | Customer inquiry-heavy brandsRetailMobile-first businesses (food delivery, ride-hailing, banking, etc.) | Offers quick help and lowers response time |
Benefits of Using Web Self-Service
A well-designed web self-service system reduces support costs, boosts customer satisfaction, and strengthens your digital self-service strategy. Here are the top benefits:

1. Reduce Support Costs
Implementing self-service tools like chatbots and knowledge bases can significantly cut operational expenses. For instance, IBM’s use of the Watson Assistant led to a 40% decrease in call center traffic. It resulted in substantial cost savings.
2. Provide 24/7 Customer Support
Self-service platforms operate around the clock, ensuring customers can access assistance whenever needed. This continuous availability meets the expectations of modern consumers who value immediate support.
3. Empower Customers to Find Answers
A significant majority of customers prefer resolving issues independently. According to a report, 73% of clients agree that the most important thing a company can do for them is to value their time. This is what self-service effectively addresses.
4. Free Up Agents for Complex Issues
By handling routine inquiries through self-service options, you can allow your customer service agents to focus on more complex and high-value tasks, enhancing overall efficiency.
5. Gather Insights to Improve Services
Self-service platforms can collect valuable data on customer behaviors and preferences. This information enables businesses to refine their services and customize offerings to meet customer needs.
Web Self-Service Examples from Leading Brands
From tech startups to global banks, businesses are deploying tools like knowledge bases, customer portals, forums, and AI assistants. Here are some examples to follow:
1. Agency Handy’s Live Chat Assistant
Agency Handy uses an AI-powered live chat widget, prominently placed on the homepage, to provide real-time support to website visitors.
Whether it’s guiding new users through features or answering pre-sales questions, the assistant responds instantly, without needing a human rep.
This improves customer experience by reducing wait times. It can also be a lead-capturing tool as prospects interact with the chatbot too.

2. Slack’s Knowledge Base
Slack’s Help Center is quick, clean, and built for self-service.
A smart search bar leads the experience. Clear categories like “Getting Started” and “Workspace Administration” guide users through tasks.
Articles mix concise steps with visuals and GIFs, making answers easy to find and follow, perfect for busy teams who want instant, no-fuss help.

3. CitiBank’s Customer Portal
Citibank’s web self-care portal offers secure, authenticated access for users to manage accounts, transfer funds, pay bills, download statements, and monitor transactions. Built with multi-factor authentication and real-time data sync, it supports digital full-service banking.

4. Notion’s Community Forum
Notion’s community forum is a structured, user-moderated space built on Discourse. It enables peer-to-peer support through tagged threads, searchable archives, and topic-specific categories.
Users contribute templates, troubleshoot advanced use cases, and surface feature workarounds. It’s a dynamic extension of Notion’s core support strategy and a feedback loop for product development.

Why Agency Handy is the Best Web Self-Service Portal for Your Business
Agency Handy is the perfect tool that lets agencies offer self-service at scale. It reduces back-and-forth communication and empowers clients to help themselves.
Here’s how it enables web self-service for your customers:
- Let clients purchase services without manual quotes
Agencies can set up a custom service catalog with transparent pricing. Clients browse, select packages or add-ons, and check out instantly, just like an online store. No sales calls, no forms, no delays.
- Accept project inputs through structured, self-guided forms
Agencies can design branded order forms, making it easy for clients to upload files, provide instructions, or select options. No more chasing down missing details over email.
- Trigger automated onboarding with client portal access
Once a client makes a purchase, the system sends an invite to a secure portal where they sign up to access their dashboard. Clients can start submitting task requests on their own.
- Task updates & Feedback in one place
Clients can submit, track, and comment on tasks in their portal. Agency Handy allows a client approval workflow, which means clients can provide feedback in their own time.
- Automate billing and eliminate payment delays
Invoices are created and sent directly through the system. Clients can view, pay, or download receipts from the portal, removing the need for follow-ups.
- Built-in support that keeps your inbox clean
Instead of fielding support emails, clients open tickets within their portal. You manage inquiries in a centralized, trackable space with internal notes and file sharing.
Pros of Agency Handy
- Self-checkout purchase from the service catalog
- Support tickets are built into the client portal
- Customers can request tasks
- Reduce time spent on sales, onboarding, and admin tasks
- Automate repetitive client communication
Final Words
In my experience, just creating a knowledge base will cut down on the tickets you get. But for that, you need data on what questions your customers ask most and where they struggle.
You need the time to analyze what to include in your Help Center and make constant adjustments.
Depending on the service you provide, a customer portal will also automate a lot of your client communication. It empowers your customer with all the information they need.
FAQs
Do small businesses benefit from self-service tools?
Absolutely. Even small teams can reduce email volume and boost client satisfaction by offering FAQs, templates, or a simple help center for recurring questions.
Can web self-service fully replace human support?
No, it can’t and shouldn’t. Web self-service handles repetitive or simple issues, but complex or emotional support cases still require human agents for empathy, context, and problem-solving.
How often should a knowledge base be updated?
Ideally, every time your product, service, or policy changes. Regular quarterly reviews also help to catch outdated content and improve the accuracy of your self-service resources.






